Analysis of Anti-Nematode Compounds in Plants
Given the large yield losses attributed to plant nematodes and the limited availability of sustainable control strategies, new plant-parasitic nematode control strategies are urgently needed. To defend themselves against nematode attacks, plants possess sophisticated multi-layered immune systems. One element of plant immunity against nematodes is the production of small molecules with anti-nematode activity, either constitutively or after nematode infection.
Lifeasible provides analysis of anti-nematode compounds in plants to help our customers worldwide in the field of plant science. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers' demands.
Analysis of Phenolic Compounds Responses to Nematode Infection
- Phenolic compounds play a major role in resistance to various plant pests and diseases. A role for phenolic compounds in nematode resistance has been suggested since at least the early 1960s. In general, higher basal and/or induced amounts of phenolic compounds have been found to correlate with nematode resistance in a wide variety of plant-nematode combinations.
- Flavonoids constitute a large class of secondary metabolites in plants. Some flavonoids play essential roles in nematode resistance by functioning as nematicides, metastatic compounds (which do not kill but inhibit their movement), repellents, or inhibitors of egg hatching.
- Lifeasible provides analysis services of phenolic compounds, including chlorogenic acid, salicylic acid, phenylphenalenone anigorufone, stilbenoids, diarylheptanoids, tannins, etc. We also provide analysis services for flavonoids, including flavonols (e.g., kaempferol, quercetin, myricetin), isoflavonoids, and pterocarpans (e.g., medicarpin, glyceollin).
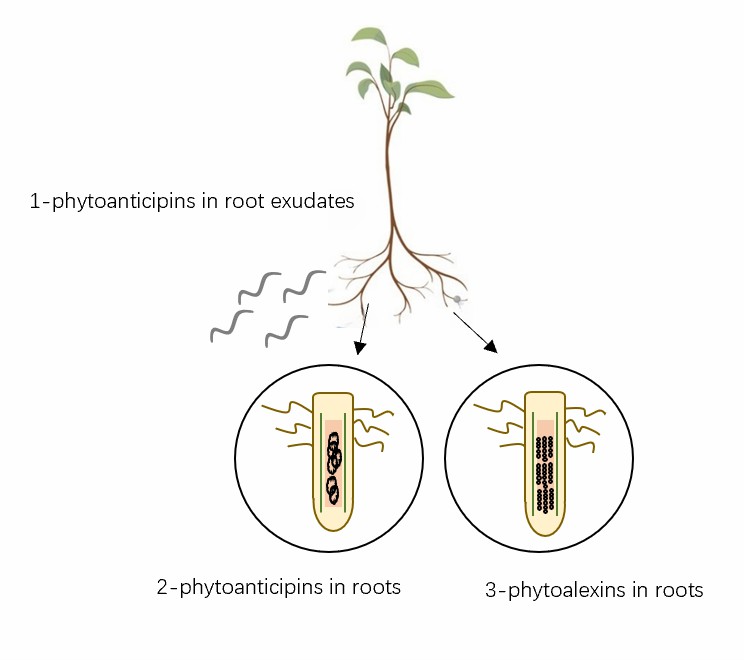 Fig.1 Three types of plant anti-nematode phytochemicals.
Fig.1 Three types of plant anti-nematode phytochemicals.
Analysis of Interruption Compounds for Plant Nematode Chemotaxis
- In addition to nematicides and metastatic compounds, interruption of nematode chemotaxis may also be an effective plant response for inhibiting or limiting nematode infection. Such as ethylene, which is normally produced after wounding and during pathogen invasion, reduces PPN attraction to the root.
- We provide analysis services of ethylene for plant nematode chemotaxis, including the effects of overproducing and insensitive ethylene on nematodes' attractiveness.
Analysis of Other Compounds Responses to Nematode Infection
- Apart from phenolic compounds, other nematocidal chemicals are produced by several nematode-antagonistic plants, such as marigolds and asparagus, which have been used for reducing nematode populations in soil.
- We provide analysis services of other compounds' responses to nematode infection, including α-terthienyl secreted by marigold roots, asparagusic acid secreted by asparagus, the broad spectrum antimicrobial isothiocyanates and indole glucosinolates from Brassicaceae family plants, etc.
Lifeasible has long-term devoted to the development and application of plant science. We are pleased to use our extensive experience and advanced platform to offer satisfied service and qualified products to satisfy each demand from our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 Three types of plant anti-nematode phytochemicals.
Fig.1 Three types of plant anti-nematode phytochemicals.