The reproductive mode of fungi is diverse and can be broadly classified into two categories: asexual and sexual. Almost all fungi can reproduce sexually, but most of the time, fungi reproduce asexually. Sexual reproduction in fungi is mainly controlled by mating-type genes, which regulate the hormonal regulation mechanism of male and female gamete cooperation and hermaphroditic affinity cells, sex differentiation, and sexual development, as well as the regulation of ascospore formation. Therefore, the in-depth study of mating-type genes is essential for understanding the sexual reproduction pattern of fungi.
The emergence of mating-type genes is an essential time in the evolution of fungi. Studying the sequence characteristics of mating-type genes and their functions and regulatory processes during sexual reproduction is essential for understanding the kinship of fungi as well as the evolution and origin of fungi. Lifeasible can provide transcriptomic analysis of mating type gene expression of fungi to help customers conduct in-depth research on fungal sexual reproduction.
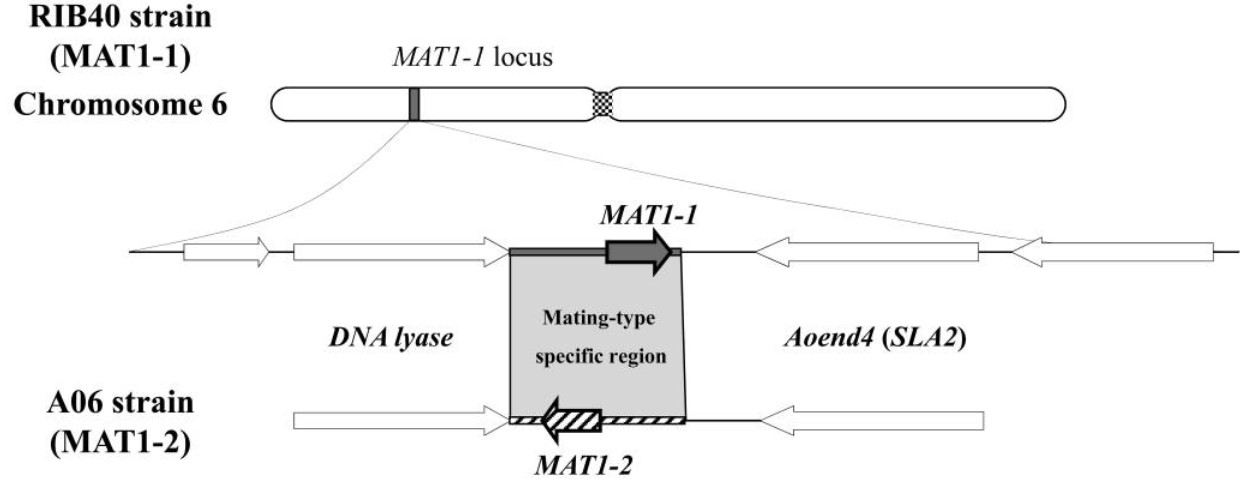 Figure 1. Schematic arrangements of the MAT loci in A. oryzae strains RIB40 and AO6. (Yan D, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Schematic arrangements of the MAT loci in A. oryzae strains RIB40 and AO6. (Yan D, et al., 2021)
Lifeasible can study some fungi's mating type genes by transcriptomic analysis to clarify the effect of mating type genes in fungi on different stages of sexual reproduction. As your trusted partner, we can meet your fungal phylogenetic analysis needs and provide you with efficient, high-quality services. If you want to know the details, please contact us.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024