Fibrous textures similar to meat have been developed through various techniques such as extrusion cooking, shearing, spinning, and 3D printing. The structuring process of plant-based meats can alter the flavor due to the high temperatures and pressures applied. In addition, off-flavors, such as soy, bitter, aftertaste, and astringency, are frequently detected in plant-based. Off-flavors in plant-based products may be inherent to the plant component (e.g., inherent off-flavor components) or may result from processing and storage (e.g., from oxidative deterioration of unsaturated fatty acids in protein-bound lipids). These off-flavors impede consumer preference and acceptance. Food scientists are already working to reduce or eliminate off-flavors in plant-based meats. In addition, it is challenging to mimic the flavors and aromas of meat products because of the extreme complexity of compounds associated with meat flavor.
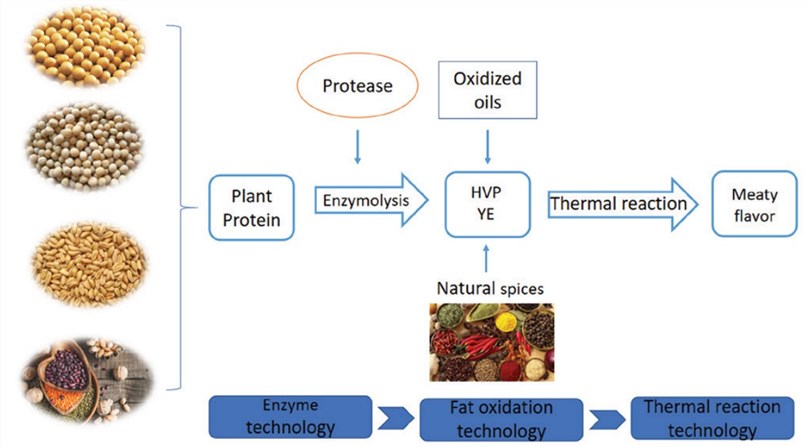 Fig.1. The process for developing flavors in plant-based meat analogues. (Li X et al., 2020)
Fig.1. The process for developing flavors in plant-based meat analogues. (Li X et al., 2020)
As quality improves, the number of flavoring agents used to replicate chicken, beef, or other meat products is too high, creating a negative taste experience for the consumer. In addition, plant-based products taste bitter and salty to consumers because of the high levels of sodium added to enhance flavor. Lifeasible is a leading partner in improving the flavor of plant-based meats. We offer a variety of solutions to prevent, reduce, or mask associated off-flavors, as well as bitter, astringent and metallic flavors. Also, minimizing the alteration of functional properties of protein isolates or concentrates. We offer methods designed to remove or reduce off-flavor compounds in plant-based meats.
Natural flavoring agents are often more acceptable than synthetic flavoring agents. We use physical methods to extract flavoring agents from natural sources. Our carefully prepared plant-based ingredients, such as hydrolyzed vegetable protein (HVP), yeast extract (YE), and natural flavors, are widely used in the formulation of plant-based meat analogs.
We offer solvent extraction methods to remove undesirable flavor substances. This method has the advantages of low cost, simple operation, and good controllability.
❖ Bean flavors and total volatiles in plant-based meats are treated with ethanol, 2-propanol, or isopropanol for bean proteins.
❖Supercritical CO2 extraction was used in combination with ethanol to remove volatile compounds and reduce the bitterness of pea flour.
Depending on the characteristics of the plant protein composition (i.e., the type of bittering compounds), we will carefully select a specific heat treatment technique for you or combine it with other bittering treatments.
Polysaccharides influence flavor release and perception by binding directly to flavor molecules and/or by trapping these molecules in the food matrix. Our team of experts experiments with incorporating polysaccharides into plant-based meats to reduce the undesirable odors and flavors associated with plant proteins.
We offer enzymatic hydrolysis technologies to reduce or eliminate off-flavors from vegetable proteins and products containing them. Our focus is optimizing the modification of protein technology functions and hydrolysis processes to avoid compromising sensory quality.
We offer fermentation technology to improve the aroma characteristics and reduce the formation of off-flavors in vegetable protein ingredients. We have successfully used this technology to mask or reduce bitter and bean-like flavors in isolated soy, pea, and lupine proteins, and related products.
Lifeasible has great potential to create plant-based meats with compelling flavors, with rigorous testing and fine-tuning throughout the process. We offer a variety of strategies for developing plant-based meats with lighter flavors (or milder tastes and odors) and fewer off-flavors. Depending on the presence of problematic flavor compounds, our team of experts will design customized options for removal or masking. It must ensure minimal loss of protein function and nutritional quality of protein components. Feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference