Recently, the forage breeding and cultivation innovation team has confirmed that the conserved threonine 3 (T3) on phosphorylated histone H3 is directly involved in flowering regulation, revealing the molecular mechanism of protein epigenetic modification regulating plant flowering. The results were published in the Plant Journal.
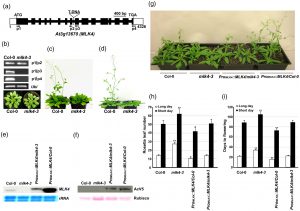
According to researcher Wang Zhen, the corresponding author of the article, casein kinase I (CK1) is a serine/threonine (Ser / Thr) kinase that is ubiquitous in eukaryotes. It is involved in the regulation of a variety of biological processes. Arabidopsis mut9 like (MLK) kinases are members of the plant-specific CK1 family. MLK1 and MLK3 can phosphorylate the highly conserved threonine (H3T3) of histone H3. The phosphorylated histone H3T3 (H3T3PH) is involved in maintaining chromosome configuration and gene/transposon silencing. The results showed that MLK4-3, a T-DNA insertion mutant of MLK4, showed delayed flowering in both long day and short day conditions, while MLK4 overexpression plants bloomed earlier. In vivo and in vitro experiments showed that nuclear protein MLK4 specifically phosphorylated histone H3T3, and its catalytic activity depended on lysine at position 175 (K175). The mutant (MLK4K175R) could not complement the late-flowering phenotype of the MLK4-3 mutant and did not affect its H3T3PH level.
Further transcriptome analysis showed that FLC, MAF4, and MAF5 were up-regulated in MLK4-3. In addition, the double mutant MLK4-3 FLC-3 flowered earlier than MLK4-3, indicating that the late-flowering phenotype of MLK4-3 requires normal expression of FLC. Chip qPCR analysis showed that MLK4-flag directly bound to FLC / MAF promoter. Compared with the wild type, the H3T3PH enrichment of FLC / MAF promoter in MLK4-3 was significantly decreased, while the RNA Pol II was significantly increased, indicating that MLK4 mediated H3T3 phosphorylation was negatively correlated with FLC / MAF expression.
This study revealed the mechanism of plant-specific casein kinase MLK4 promoting flowering of Arabidopsis thaliana by phosphorylating histone H3 and inhibiting FLC / MAF at the transcriptional level. MLK4, as a key cross point of the flowering regulation network, participates in multiple flowering pathways, and further exploration of its function is of great significance for precise regulation of plant flowering.
Reference
Zhen Wang; Junmei Kang; et al. MLK4‐mediated phosphorylation of histone H3T3 promotes flowering by transcriptional silencing of FLC/MAF in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2020 Dec 6. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15122.