Control of Plant Nematodes by Toxin-Producing Fungi
All fungi capable of producing toxic nematode toxins are known as toxin-producing fungi; they are divided into two main categories, exclusively toxic and partly toxic. To date, nearly 230 metabolites active against nematodes have been isolated from more than 280 strains of 150 genera, including quinones, alkaloids, macrolides, terpenes, peptides, fatty acids, and furans produced by some of the fungal species of Basidiomycetes, Ascomycetes, and Hemiptera.
Lifeasible provides analysis services of fungi that poison plant nematodes to help our customers worldwide in the field of plant science. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers' demands.
Analysis of Trichoderma Fungi
- Trichoderma is one of the most studied and effective biocontrol fungi in the world and plays an important role in agricultural production. They not only parasitize nematode eggs and larvae but also produce many secondary metabolites with nematocidal activity, including trichodermin, β-vinylcyclopentane-1α, 3α-diol, 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one, 4-(2-hydroxyethyl) phenol, and extracellular hydrolases, including serine proteases, chitinases, proteases, etc. for the control of phytopathogenic nematodes.
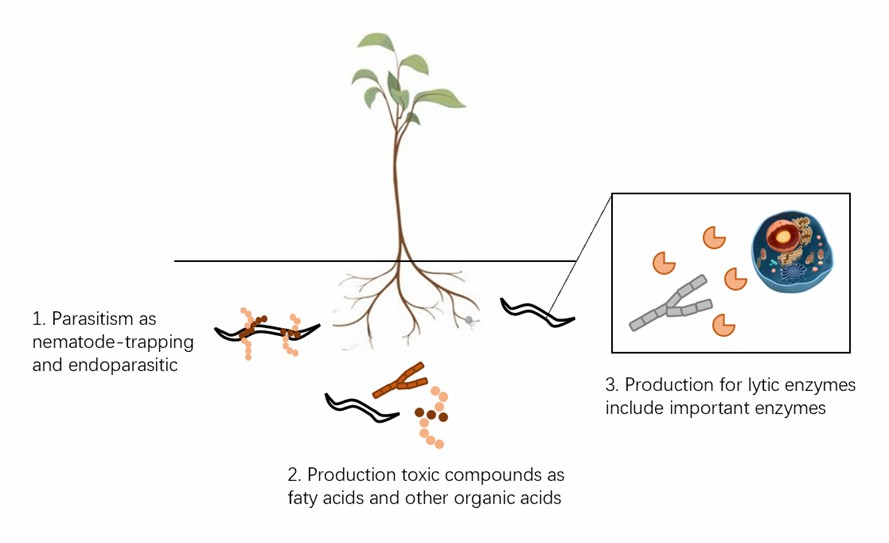 Fig.1 The types of mechanisms used by fungi to infect nematodes.
Fig.1 The types of mechanisms used by fungi to infect nematodes.
- Lifeasible provides analysis of Trichoderma that poisons plant nematodes, including T. atroviride, T. harzianum, T. tomentosum, T. virens, and T. asperellum, all of which have inhibitory effects on plant parasitic nematodes.
- We have also helped customers to study the toxicological effects of fermented solutions of Trichoderma on nematodes, including the disintegration of nematode eggs and larval body walls, the inhibition and delaying of egg hatching, and the vacuolization of larvae.
Analysis of Other Toxin-Producing Fungi
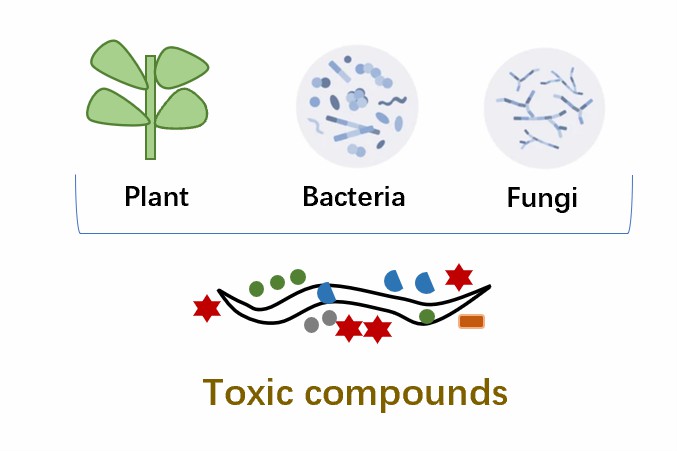 Fig.2 Attack by spores and various toxic and lethal metabolites released by fungi.
Fig.2 Attack by spores and various toxic and lethal metabolites released by fungi.
- Metabolites from the fermentation broth of some toxin-producing fungi have been reported to be strongly lethal to nematode larvae. Their semi-lethal concentrations are about the same as those of chemically synthesized nematicides, and they also inhibit egg hatching.
- We provide analysis of other toxin-producing fungi, including the metabolite ChA from Chaetomium globosum, the metabolites 3-hydroxypropionic acid from Phomopsis phaseoli and Melanconium betulinum, the metabolite Cerebroside A from Paecilomyces lilacinus, and the new skeletal macrolide compounds isolated from Talaromyces thermophilus. We also offer analysis services for the non-pathogenic fungus Fusarium oxysporum, which effectively suppresses nematode populations.
Lifeasible provides cost-effect, high-quality, and hassle-free services to our clients worldwide. We provide our clients with direct access to our experts and prompt responses to their inquiries. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 The types of mechanisms used by fungi to infect nematodes.
Fig.1 The types of mechanisms used by fungi to infect nematodes. Fig.2 Attack by spores and various toxic and lethal metabolites released by fungi.
Fig.2 Attack by spores and various toxic and lethal metabolites released by fungi.