Pathogenicity Analysis of Plant Nematodes
Nematodes are widely distributed in every corner of the world, and most live freely. Although there is an early understanding of the living parasitic nematodes, the research history of the plant threadworms is very short. By the time it was realized that many plant diseases were caused by plant nematodes, they were already causing huge economic losses worldwide. Plant nematodes cost the world $8 billion a year in economic losses, about 10 percent of total agricultural losses.
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide pathogenicity analysis of plant nematodes. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
- The developmental processes of pathogenesis are related to the way that nematodes adversely affect the host-either as superficial feeders or as endoparasites that induce syncytia or giant cells. Some nematodes cause extreme galling. Once in contact with the roots, nematodes may feed either on the surface of roots as ectoparasites or internally after penetration of roots as migratory or sedentary endoparasites.
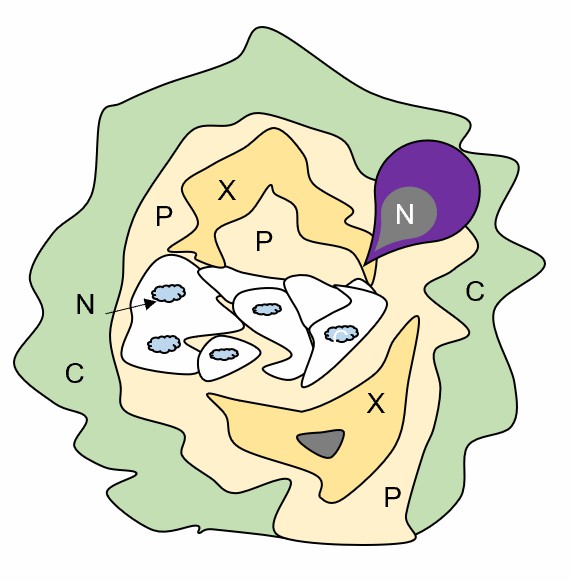 Fig.1 Cross-section of a 4-week-old gall induced by plant nematodes.
Fig.1 Cross-section of a 4-week-old gall induced by plant nematodes.
- In many cases, nematodes act alone as primary pathogens, but in other cases, they interact with other organisms in disease complexes or serve as vectors for viruses.
- Lifeasible provides analysis of the pathogenic effects of nematodes, including attraction of nematodes to the host, feeding sites and host penetration, nematode feeding processes, damage of host tissue, interactions with other pathogens, interactions with viruses and vector relationships, etc.
- In the later stage of pine wood nematode disease, pine wood nematode changed from the parasitic stage to the saprophytic stage after the pine tree died completely. The nematode feeding on the fungi in a pine tree, which maintained the survival and reproduction of the pine wood nematode population and provided the possibility for reinfection.
- We provide pathogenic effects of nematode endogenous microorganisms, including the effect on nematode populations and the correlation between endogenous microbial diversity and plant resistance.
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 Cross-section of a 4-week-old gall induced by plant nematodes.
Fig.1 Cross-section of a 4-week-old gall induced by plant nematodes.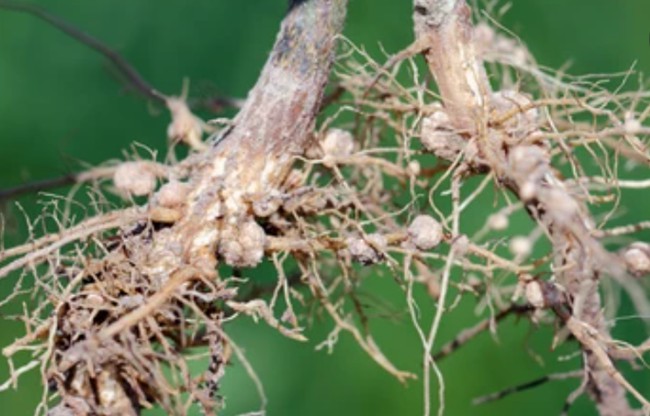 Fig.2 Nematode-infected root systems.
Fig.2 Nematode-infected root systems.