Analysis of the Predatory and Parasitic Effects on Nematodes
Inter-root microecology achieve suppression of plant nematode disease through the interaction between rhizosphere microorganisms. Nematodes in soil are subject to infections by bacteria and fungi. Predatory microorganisms are mainly fungi, while parasitic microorganisms can contact the epidermis of root knot nematodes through spores or enter directly into the root knot nematodes. This creates the possibility of using soil bacteria to control nematodes. An effective natural enemy of nematodes is nematophagous bacteria ubiquitous with wide host ranges. These organisms have been isolated from the soil, plant tissues, cysts, and eggs of nematodes.
As a professional biology service provider, Lifeasible offers an analysis of the predatory and parasitic effects of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant nematodes with decades of experience. Our experts will answer your questions comprehensively and carefully and help you solve the problems in your studies. We guarantee satisfied and reliable results for our customers all over the world.
The Predatory Effects of Rhizosphere Microorganisms
- Nematophagous fungi are the largest and the most studied group of fungi involved in the biological control against plant‐parasitic nematodes. Among nematophagous fungi, which have been tested for their efficacy in controlling nematodes, some are obligate parasites; others are facultative or opportunistic parasites.
- Lifeasible provides an analysis of the role of predatory effects of rhizosphere microorganisms, including female nematodes, thick-walled sporozoites, adhesive secretions, sticky branches, adherent spores, adhesive knobs, and others.
- In addition, we help analyze the mechanisms that inhibit nematode growth and development, such as contact killing in a physical manner or chemical killing in the presence of lysozyme.
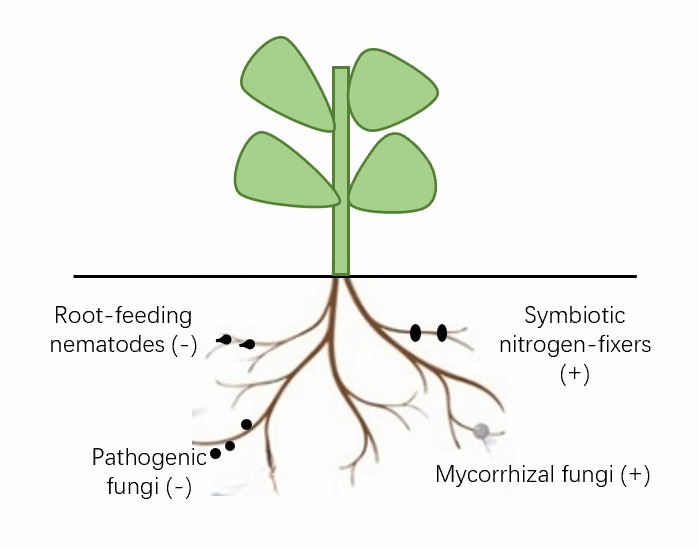 Fig.1 The impacts of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant performance.
Fig.1 The impacts of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant performance.
The Parasitic Effects of Rhizosphere Microorganisms
- Plant nematodes cause considerable damage to various plants. The rhizosphere microorganisms can affect the invasion and reproductive success of plant-parasitic nematodes, thus affecting plant damage.
- We provide analysis of the role of parasitic effects of rhizosphere microorganisms, helping our customers study different parasitic modes, such as contact with the nematode epidermis by spores and entry into the nematode directly. Our list of services also involves mechanistic aspects, such as inhibition of egg hatching, killing nematode eggs, digestion and absorption of nutrients within the eggs, etc.
Lifeasible offers analysis services for the predatory and parasitic effects of rhizosphere microorganisms with customized delivery strategies and precise design. Our advanced technical platforms help our clients solve the problems they may encounter in research based on decades of experience. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 The impacts of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant performance.
Fig.1 The impacts of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant performance.