In the plant-soil-microbe ecosystem, an imbalance of rhizosphere microorganisms plays an important role in disease development. Some soil-borne pathogens, such as root nematodes, Fusarium glauca, Fusarium acnes, etc., are closely associated with soil microbial imbalances. Around the root system of plants, soil microorganisms, and pathogens interact with each other and affect plant health. Inter-root microecology can achieve nematode suppression through interactions between rhizosphere microorganisms.
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide a mechanism analysis of plant response to nematodes. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
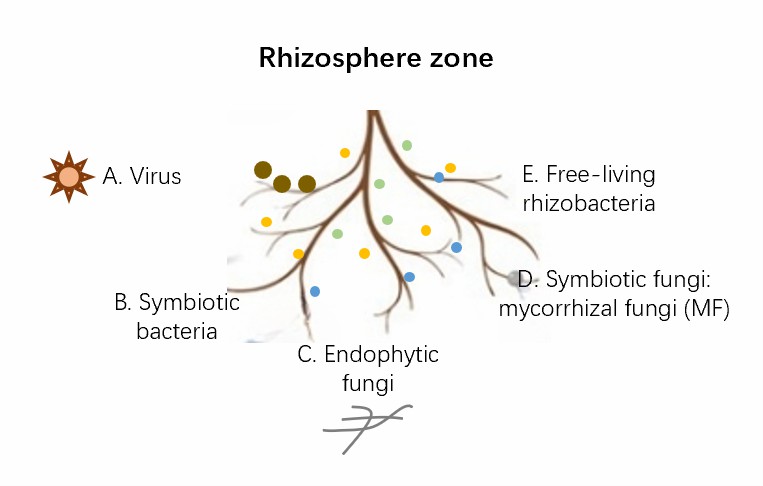 Fig.1 Microbial community of rhizosphere.
Fig.1 Microbial community of rhizosphere.
Rhizosphere microorganisms can occupy signal recognition sites faster and can stably around the root system, making the root-knot nematode less efficient in recognizing the root system of the host plant. We provide an analysis of competitive effects on nutrient and spatial sites, which can reduce plant infection to inhibit disease development.
Antagonistic microorganisms are capable of direct penetration of root-knot nematodes and egg walls. We provide analysis of active substances to kill nematodes, including enzymes that produce ablative effects, secondary metabolites with toxic effects, and others.
The rhizosphere microorganisms are capable of producing systemic resistance in plants, and the production of induced systemic resistance (ISR) can be useful against a wide range of common pathogens. We provide analysis of the induction of resistance in plant systems, including resistant enzymes and plant secondary metabolites, and so on.
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.