On November 9, 2023, Science published a research paper titled "Plant cell wall patterning and expansion mediated by protein-peptide-polysaccharide interaction" online. This study found that the LRX8-RALF4 complex can specifically interact with demethylated pectin in a charge-dependent manner in plants, resulting in the formation of the LRX8-RALF4-pectin tripartite network architecture and playing an important role in maintaining the integrity and expansion of the pollen tube cell wall, which reveals a new function of RALF4 as a structural component of the cell wall to maintain the integrity of the pollen tube cell wall.
In view of the great significance of this research, Science published a short review article titled "A signaling peptide locks pollen tube walls" online on the same day.
Plants need to assemble cell wall polysaccharides into specific patterns during growth. During cell expansion, demethylesterification modulates homogalacturonan charge and plays an important role in controlling cell wall mechanics. At the same time, tight regulation of cell expansion requires rapid feedback loops of cell wall deposition and remodeling to avoid loss of cell wall integrity. Studies have shown that the small peptide RALF4 interacts with demethylesterified homogalacturonic acid and is required for cell wall patterning. In addition, the complex formed by the interaction between RALF4 and its cell wall-anchored protein LRX8 is crucial for the integrity of the cell wall during pollen tube growth. However, how RALF4 is connected to the cell wall is unclear.
This study first demonstrated that the LRX8-RALF4 complex is in a heterotetrameric configuration in plants and exhibits a dendritic distribution. It was further found that the LRX8-RALF4 complex can interact specifically and with high affinity with demethylesterified pectins through the polycationic surface of RALF4 in a charge-dependent manner.
Using high-resolution microscopy, the study found that the interaction between LRX8-RALF4-pectin in pollen tubes exerts a cohesive effect, causing the cell wall polymers to form a mesh network, thereby generating and maintaining a stable reticulate tripartite network architecture.
So, what effect does this tripartite network architecture have on the cell wall? This study found that the LRX8-RALF4-pectin tripartite network architecture is critical for pollen tube cell wall integrity and expansion, indicating that RALF4 is not only a small peptide signal, but also a cell wall structural component that promotes the patterning of cell wall polysaccharides into strong multimeric assemblies as part of LRX8-RALF4-pectin.
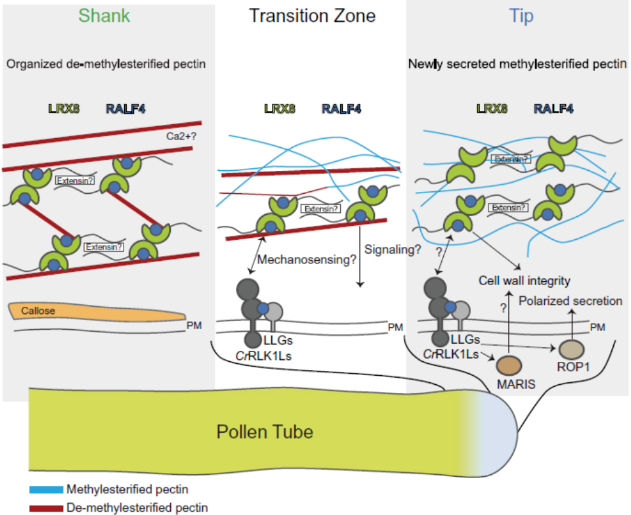
In summary, this study illustrates the mechanism of RALF4 in maintaining pollen tube cell wall integrity. At the tip, the transmembrane proteins CrRLK1L and LLG sense RALF4/19 to activate downstream MARIS and ROP1 proteins, thereby regulating actin dynamics and promoting polarized secretion of cell wall components and their regulatory proteins. In the transition zone, pectin is converted to the demethylesterified form by pectin methylesterase, which is then recognized by the LRX-RALF4 complex and interacts to form a criss-crossing filamentous network that contributes to the formation, strengthening, and expansion of cell walls. At the shank, pectin demethylesterification is completed and the LRX-RALF4-pectin complex remains an integral part of the pollen cell wall, possibly acting as a load-bearing system during pollen tube expansion to compensate for its low cellulose content.
Reference:
Moussu, S., et al. Plant cell wall patterning and expansion mediated by protein-peptide-polysaccharide interaction. Science. 2023, 382(6671): 719-725.
Mohnen, D. A signaling peptide locks pollen tube walls. Science. 2023, 382(6671): 648-649.