Nematode Companion Microorganisms Producing Plant Toxins
There is a wide variety of nematode associated microorganisms, with three main groups, Pantoea, Pseudomonas, and Peptostreptococcus, isolated from different infected areas and from different species of diseased wood. The nematodes and the microorganisms they carry have evolved in synergy over a long time, resulting in various mutualistic relationships ranging from mutually beneficial symbiosis to antagonism. Nematode companion microorganisms can produce phytotoxins that indirectly influence the pathogenic processes of nematodes.
Lifeasible develops an advanced platform that provides customers worldwide, covering analysis services for nematode companion microorganisms that can produce plant toxins. We customize featured services according to customer needs with decades of experience in plant protection. In addition, we deliver satisfactory and reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
Plant Toxin Secreted by Pseudomonas Fluorescens
- The toxin secreted by Pseudomonas fluorescens is a cyclic dipeptide, a flagellin-like peptide chain, which is toxic to both the plant tree and the cell suspension.
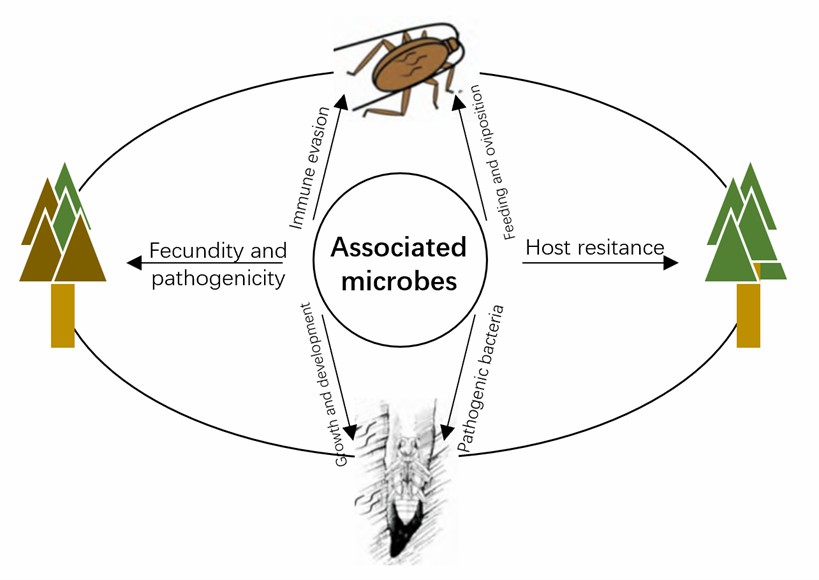 Fig.1 Interaction between companion microorganisms and plant nematodes.
Fig.1 Interaction between companion microorganisms and plant nematodes.
- This substance promotes the multiplication of nematodes and their associated micro-organisms, for which Lifeasible offers related analysis service. For example, using the flagellin peptide chain treatment and untreated healing tissues as a control, dead plant healing tissues are observed, and the number of nematodes and Pseudomonas fluorescens in the tissue is recorded.
- In addition, we further offer the service of studying the relationship between the occurrence of nematode diseases and companion bacteria. Inoculation with sterile nematodes alone fails to cause browning of the healing tissue and wilting of sterile seedlings, whereas inoculation with a mixture of sterile nematodes and nematode-carrying bacteria, respectively, cause severe disease in both sterile seedlings and healing tissue.
Analysis of Other Companion Microorganisms
- We help analyze Bacillus cereus, a bacterium that produces phenylacetic acid, which promotes the synthesis of benzoic acid and its conjugates in large quantities in plants and induces death in the host. Our service also includes Burkholderia arboris, which produces Pseudomonas aeruginosa and is highly toxic to saplings and healing tissue.
- Our list of services also includes Serratia sp., Enterobacter sp., and Pantoea sp., which can cause wilting and yellowing of needles and leaves. Most importantly, the role of companion microorganisms in the pathogenesis of nematodes is analyzed specifically in relation to different strains, tree species, and site environments.
Lifeasible offers professional services covering nematode companion microorganisms that secrete plant toxins to meet your research needs. With years of experience in plants, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties and conduct research. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 Interaction between companion microorganisms and plant nematodes.
Fig.1 Interaction between companion microorganisms and plant nematodes.