Analysis of Effector Proteins in Plant Nematodes
Plant nematodes are one of the important pathogens causing plant diseases. They have the characteristics of long survival time, wide transmission routes, strong adaptability, and serious harm. During infection, plant nematodes secrete many proteins to the host body, which play a vital role in the invasion, establishment, and maintenance of feeding sites and host defense response. Such secreted proteins are called effector proteins.
Lifeasible provides services covering various mechanism analyses of effector proteins in plant nematodes to our customers worldwide. With extensive experience and expertise in plant science, we are committed to providing you with timely and high-quality deliverables.
- Plant cell walls can protect plant cells against potential invaders, which is the natural physical barrier of plant cells. The main components of the plant cell wall include cellulose, hemicellulose, and the pectin layer.
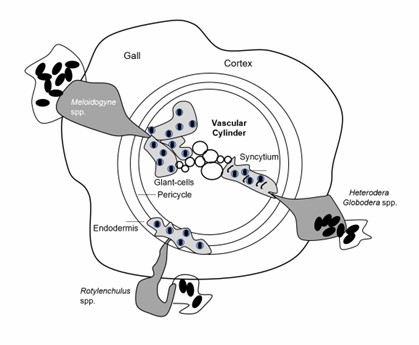 Fig.1 Feeding cells formed by sedentary plant nematodes.
Fig.1 Feeding cells formed by sedentary plant nematodes.
- Lifeasible provides mechanism analysis of host cell wall degradation by effector proteins in plant nematodes, primarily cellulases, dilatants, and cellulose-binding proteins, involved in cell wall synthesis, degradation, and modification.
- During nematode infection, host plants activate the ROS biosynthesis mechanism to induce the suicidal programmed death of cells at the feeding site and cause hypersensitivity reactions to kill pathogens at the infected site, thus limiting the spread of pathogens.
- We provide mechanism analysis of regulating host basal immune response by effector proteins in plant nematodes, which focus on nematode effect-proteins that inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS), callose deposition, and expression of defense-critical genes in plant cells.
- Except for a few effector proteins that can stimulate plant immune response, more effector proteins have been found to suppress or overcome host immune response, which is conducive to the infection and parasitism of plant nematodes.
- We provide a mechanism analysis of inducing host immune response by effector proteins in plant nematodes, including some non-toxic genes that activate the immune response. We also provide analysis of SGC, MSP, MIF, and other genes that suppress immune responses.
We provide mechanism analysis of posttranslational modification mediated by effector proteins, including phosphorylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, proteolysis, and histone modification.
We help our customers analyze the mechanism of regulating plant hormones by effector proteins, such as auxin, cytokinin, salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, ethylene, and so on.
Lifeasible has been dedicated to planting science for many years. We'll finish your studies on time and within budget. We guarantee the confidentiality and sensitivity of our customer's data. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 Feeding cells formed by sedentary plant nematodes.
Fig.1 Feeding cells formed by sedentary plant nematodes.