Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production is one of the earliest reactions in plant-nematode interactions. Reactive oxygen species signal transduction in plants can cause programmed cell death and hypersensitivity. Therefore, plant nematodes secrete a series of antioxidants and redox enzymes to resist host ROS damage. In addition, they also can inhibit callose deposition and expression of defense-critical genes in host cells.
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide the mechanism analysis of regulating host basal immune response by effector proteins in plant nematodes. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
Resisting Host ROS Damage
- During nematode infection, host plants activate the ROS biosynthesis mechanism to induce the suicidal programmed death of cells at the feeding site and cause hypersensitivity reactions to kill pathogens at the infected site, thus limiting the spread of pathogens.
- Plant nematodes secrete a series of antioxidants to protect against host ROS damage. Lifeasible provides an analysis of antioxidants secreted by plant nematodes, including glutathione (GST), peroxidase (PO), thioredoxin (TRX), cytochrome C-peroxidase (CPX), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), etc.
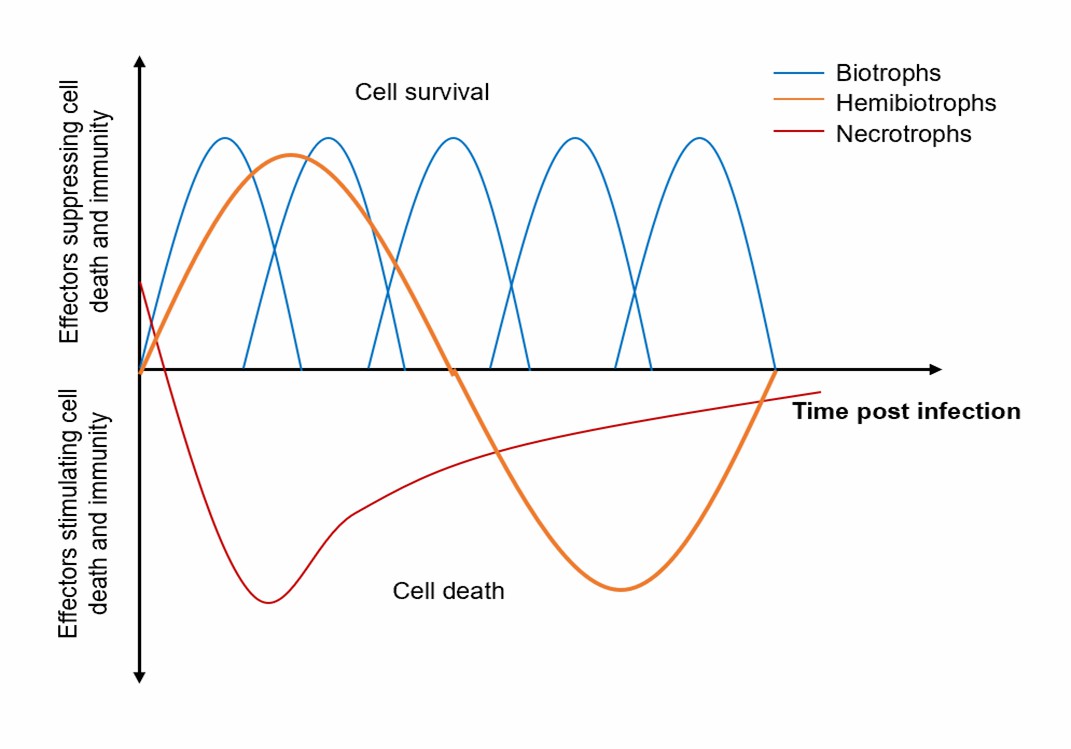 Fig.1 Waves of effector expression over time and pathogen type.
Fig.1 Waves of effector expression over time and pathogen type.
- Likewise, plant nematodes secrete a series of effector proteins to protect against host ROS damage. Lifeasible analyzes effector proteins secreted by plant nematodes, including 10A06, MjTTL5, Mg01965, and so on. We also analyze their interaction mode to improve the activity of reactive oxygen-degrading enzymes in host plants, promote the degradation of hydrogen peroxide, and thus inhibit the basic immune response of host plants.
Inhibiting Host Callose Deposition
- Callose deposits usually occur between the plasma membrane and cell wall at the site of pathogen invasion to slow the attack and spread of pathogens.
- We provide an analysis of effector proteins secreted by plant nematodes that can inhibit host callose deposition, such as MiCRT, MiMsp40, Mh265, and others induced by flg22.
Inhibiting the Expression of Host Defense Genes
- Effector proteins secreted by plant nematodes can directly interact with disease-course-related proteins to inhibit the resistance of pathogenesis-related proteins.
- We provide an analysis of effector proteins secreted that can inhibit the expression of defense genes, such as MO237, CRRSP55, Hg30C02, HgGLAND4, and others. We also analyze the interaction pattern with pathogenesis-related proteins, which can inhibit the host defense response.
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Our products/services are For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use!
 Fig.1 Waves of effector expression over time and pathogen type.
Fig.1 Waves of effector expression over time and pathogen type.