Plant nematodes are devastating pests that cause high-yield loss in agriculture. Plant nematodes secrete various effector molecules, which play an important role in parasitism. They secrete various plant immunosuppressants, enzyme inhibitors, and other proteins needed to establish feeding sites. Except for a few effector proteins that can stimulate plant immune response, more effector proteins have been found to suppress or overcome host immune response, which is conducive to the infection and parasitism of plant nematodes.
Lifeasible provides mechanism analysis of regulating host-induced immune response by effector proteins to help our customers worldwide in plant science research. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers’ demands.
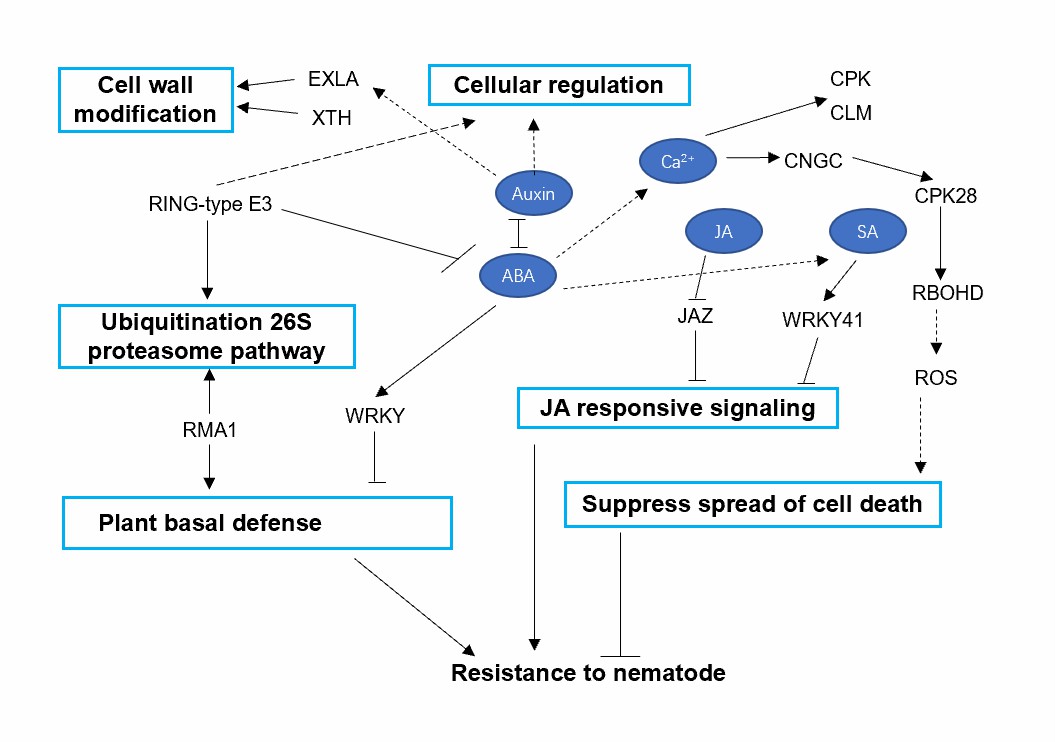 Fig.1 Model illustrating the interplay involved in host defense responses.
Fig.1 Model illustrating the interplay involved in host defense responses.
Lifeasible provides cost-effective, high-quality, and hassle-free services to our customers worldwide. We provide our clients with direct access to our experts and prompt responses to their questions. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024