Nematodes are non-segmented, elongated roundworms that are colorless, without appendages, and usually microscopic. There are non-beneficial and beneficial (e.g., entomopathogenic) nematodes. Non-beneficial nematodes cause damage to crops and other types of plants. Beneficial nematodes cause damage to soilborne insect pests yet are not harmful to humans, animals, plants, or earthworms and can therefore be used as biological control organisms. Beneficial nematodes are also referred to as 'entomopathogenic' (causing disease within an insect) or 'insecticidal' (ability to kill insects).
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide a mechanism analysis of plant response to nematodes. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
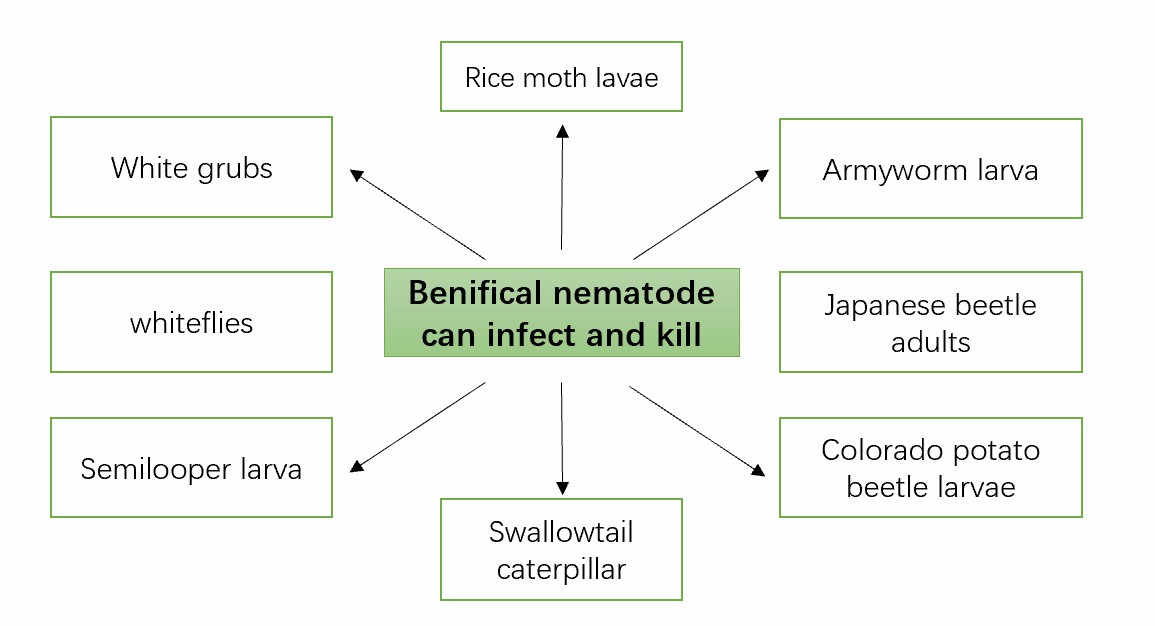 Fig.1 Diagram showing that the beneficial nematodes can infect and kill various stages of their host insects.
Fig.1 Diagram showing that the beneficial nematodes can infect and kill various stages of their host insects.
Currently, beneficial nematodes are increasingly used in life and production, and their control effect is closely related to some ecological factors, so ecological research is also developed. We provide an analysis of ecological factors associated with beneficial nematodes, such as soil temperature, moisture, soil type, and natural enemies.
We provide analysis of integrated control with beneficial nematodes, including a single use of beneficial nematodes for control, the application of beneficial nematodes in combination with pesticides for pest control, application of beneficial nematode symbiotic bacteria for pest control.
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Why Do Plants Blush When They Are Hungry?
April 26, 2024
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024