Telomeres are the protective caps located at the ends of our chromosomes, which consist of repetitive DNA sequences and associated proteins. Telomeres naturally shorten with each cell division, eventually leading to cellular senescence or cell death. However, various external factors, including stress, have been found to accelerate this telomere-shortening process. These stresses include drought, high salinity, extreme temperatures, and others.
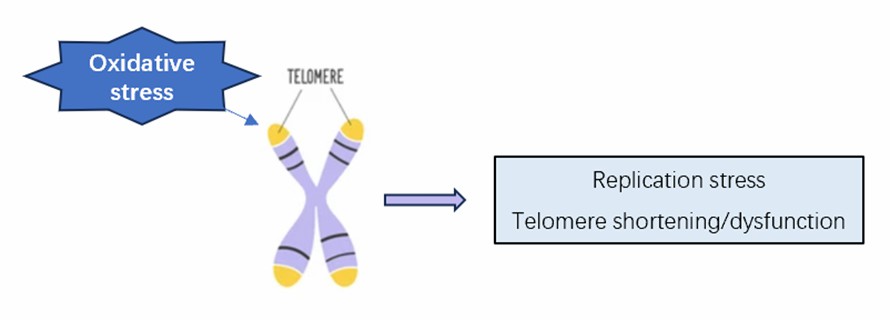 Fig. 1 Plant telomere shortening due to oxidative stress.
Fig. 1 Plant telomere shortening due to oxidative stress.
Lifeasible utilizes state-of-the-art techniques and cutting-edge research methodologies to analyze telomere length dynamics under stress conditions. Our advanced facilities and equipment allow for accurate and precise measurements, ensuring reliable data interpretation.
Lifeasible employs several methodologies for telomere length measurement to investigate stress-induced telomere shortening, including, but not limited to, those in the following tables.
| Methods | Details |
| Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) | qPCR utilizes specific primers for amplifying telomere repeats and a single copy gene (often referred to as a reference gene) from the same genomic DNA template. The ratio of telomere to the reference gene provides a relative measure of telomere length. |
| Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) | FISH allows visualization of telomeres using fluorescently labeled probes that specifically bind to the telomeric DNA sequence. Researchers can compare the telomere length between stressed and non-stressed samples by quantifying the fluorescence intensity. |
To study stress-induced telomere shortening in plants, we help our customers draw up a well-designed experimental approach to meet their scientific demands.
Lifeasible, with its expertise and dedication to scientific advancement, is dedicated to unraveling the mysteries of stress-induced telomere shortening. If you are interested in our services or have some questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024