To adapt to changing environmental conditions, plants have evolved complex tolerance mechanisms to integrate various stress signals and help plant growth and development. It is well known that the plant endomembrane system plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis in response to environmental stress. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is one of the largest, most complex, and structurally variable organelles found in eukaryotic cells. It is a central organelle involved in lipid metabolism, Ca2+ homeostasis, and the synthesis and folding of secreted and transmembrane proteins, which are essential for sensing and transducing environmental signals.
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide an analysis of the plant endoplasmic reticulum involved in biotic and abiotic stress, including innate immunity, salt stress, heat stress, AB pathway, and others. We always deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
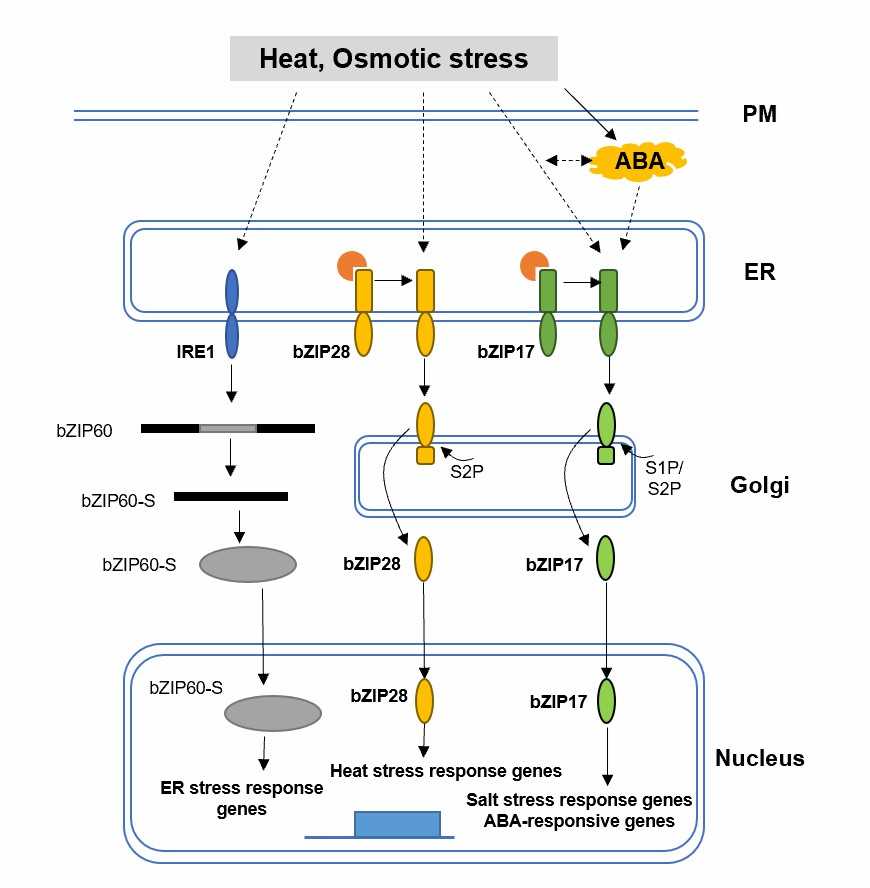 Fig.1 ER stress responses to heat, osmotic stress, and stress-related hormones in plants.
Fig.1 ER stress responses to heat, osmotic stress, and stress-related hormones in plants.
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024