An important aspect of innate immunity in eukaryotes involves rapidly detecting non-self-structures originating from potential microbial invaders. Plants monitor encounters with potential threats derived from surrounding microbes by using two classes of immune receptors, the first is pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that directly recognize their cognate microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs), and the second is disease resistance (R) proteins that recognize the actions or structures of isolate/strain-specific pathogen effectors.
Lifeasible offers comprehensive services covering a wide range of cutting-edge technologies to advance your projects. Our scientists have developed a series of innovative solutions to help analyze the role of plant endoplasmic reticulum in innate immunity.
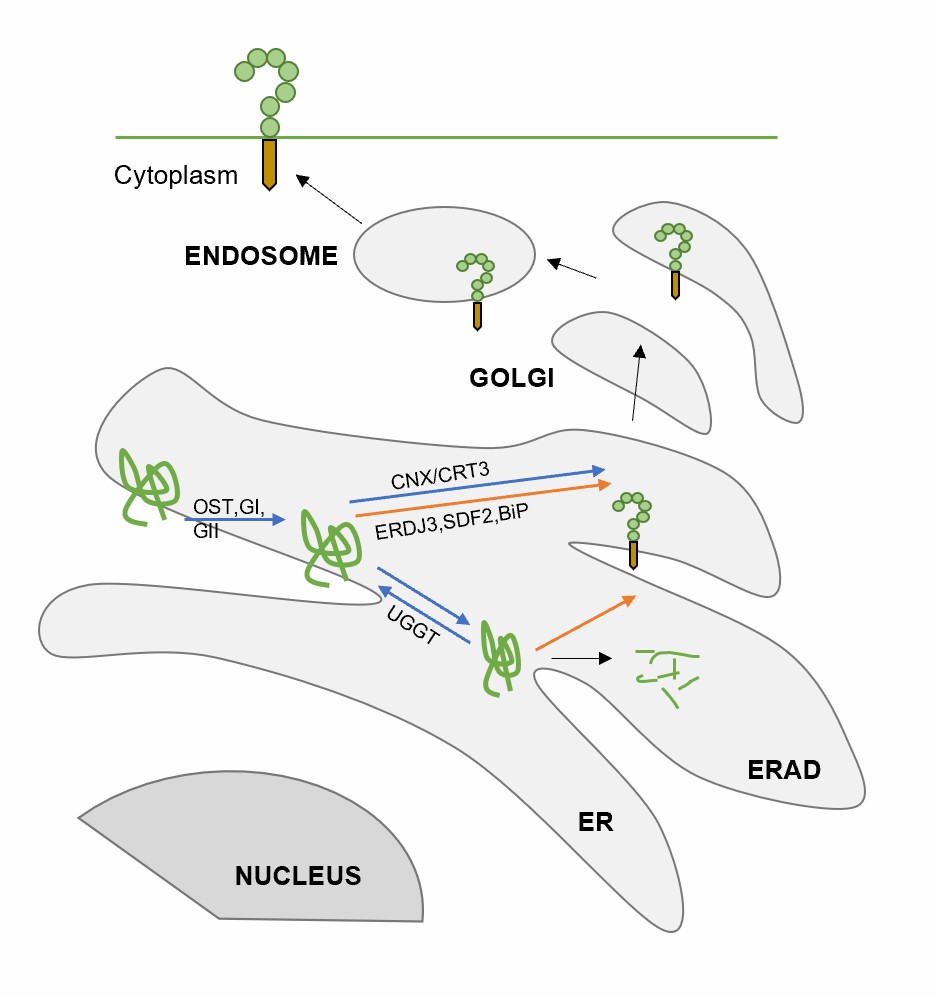 Fig.1. Processing of receptor kinases via the lectin and luminal-binding protein (BiP) chaperone complex.
Fig.1. Processing of receptor kinases via the lectin and luminal-binding protein (BiP) chaperone complex.
Lifeasible has extensive experience and expertise in plant science. We are committed to providing you with timely and high-quality deliverables. At the same time, we guarantee the cost-effectiveness, completeness, and simplicity of the report. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Why Do Plants Blush When They Are Hungry?
April 26, 2024
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024