Among the different environmental inputs, heat stress (HS) is a major factor limiting crop productivity and plant geographic distribution. The HS has a negative effect on seed germination, photosynthetic capacity, cell growth and division, and crop yield and quality. Nonetheless, plants have evolved complex molecular networks that adjust their cellular metabolism to cope with heat stress. The deleterious effect of heat stress is the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Thus, unfolded protein sensors in the ER are thought to play an essential role in heat tolerance.
Lifeasible is committed to analyzing the role of plant endoplasmic reticulum in heat stress for scientific and clinical purposes. Our experienced scientists and technicians can provide comprehensive customized services for analysis at all stages. With novel strategies and proprietary features of our platform, we can adjust to meet the needs of each client.
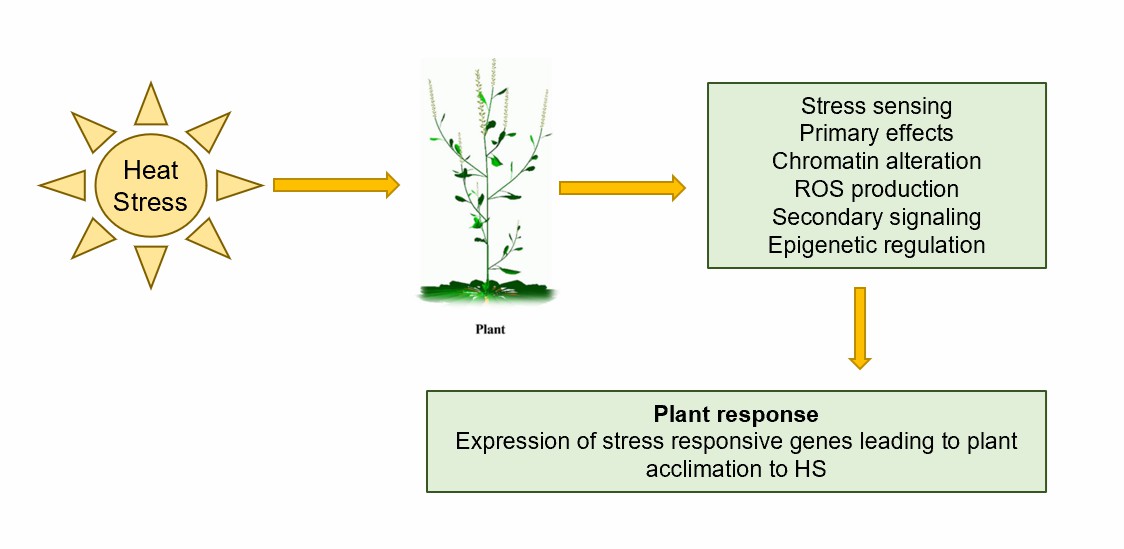 Fig.1. A generalized depiction of the temperature sensing mechanism in plants.
Fig.1. A generalized depiction of the temperature sensing mechanism in plants.
Lifeasible is dedicated to bringing decades of valuable experience to help our clients. Our customers will work with our professional teams who can totally understand and have conquered the challenges you are faced with. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024