Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) technology mainly relies on recombinant enzymes that bind single-stranded nucleic acid, single-strand binding protein, and strand displacement DNA polymerase. The recombinase binds to the amplification primer to form a recombinase primer complex. After that, the recombinase is hydrolyzed from the complex, the 3' end primer is exposed. It binds to DNA polymerase, and the DNA begins to replicate and extend, forming two new complementary double-stranded DNA, thus achieving exponential amplification of the target region on the template.
Lifeasible develops an advanced platform that provides services to customers worldwide covering the detection of plant nematodes by recombinase polymerase amplification. We customize featured services according to customer needs with decades of experience in plants. In addition, we deliver satisfactory and reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
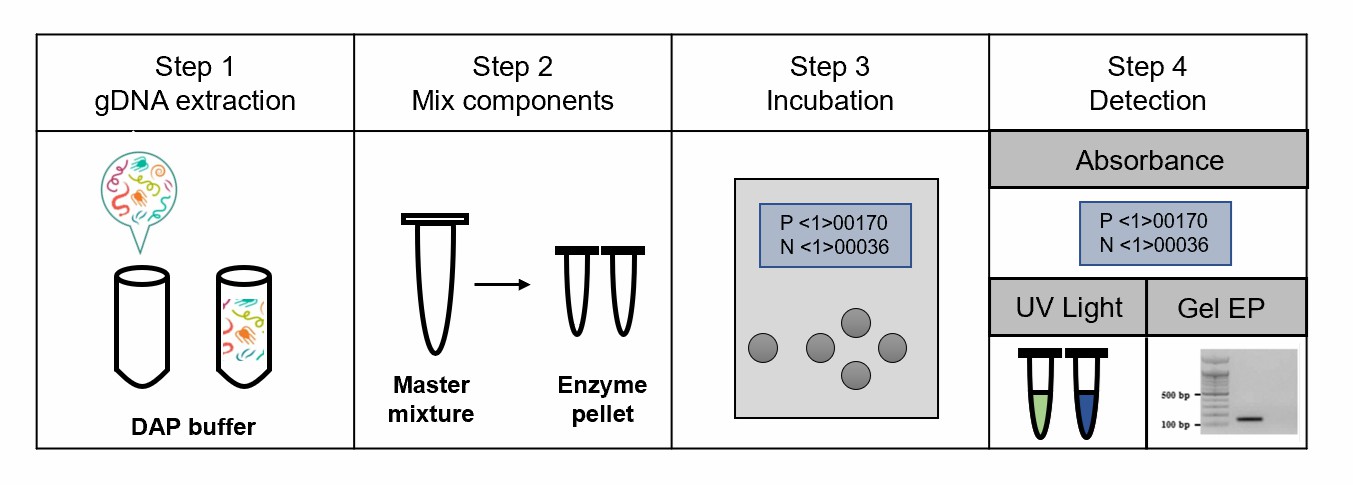 Fig.1 Schematic of the RPA assay for plant nematodes in the field.
Fig.1 Schematic of the RPA assay for plant nematodes in the field.
| Steps | Operation Methods |
| DNA Extraction |
|
| Composition and Procedure of the RPA Assay |
|
| The Specificity Test of the RPA Assay | A specificity test of the RPA assay is conducted to confirm the primers that could amplify the specific fragment from plant nematodes but not from the others. |
| The limit of the Detection Test of the RPA Assay | Tenfold serial dilutions of DNA from nematodes are used to determine the detection limit of RPA. |
Lifeasible offers professional services covering the detection of plant nematodes to meet your research needs. With years of experience in plants, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties and conduct research. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024