Lifeasible is dedicated to helping study the role of effectors in plant-pathogen interactions, and we offer customized services to help study the role and mechanisms of non-proteinaceous effectors.
Effector proteins make up the bulk of effectors. Studying effector proteins provides insight into the majority of plant-pathogen interactions. However, pathogen secondary metabolites (SMs) and small interfering RNAs (sRNAs), as non-proteinaceous effectors, also play important roles in plant-pathogen interactions. Some of the roles of non-proteinaceous effectors produced by fungi are illustrated in Fig. 1. Many studies have found that secondary metabolic effector (SME) profiles are highly specialized and unique for each plant-pathogen interaction. And the specific plant gene silencing induced by sRNAs is also unique. Lifeasible fuels the study of these non-proteinaceous effectors and offers customized services to study the unique plant-pathogen interactions they may cause. Although, some non-proteinaceous effectors can promote infiltration by influencing the microbial community surrounding the plant. Here we help to investigate the direct interaction between non-proteinaceous effectors and plants.
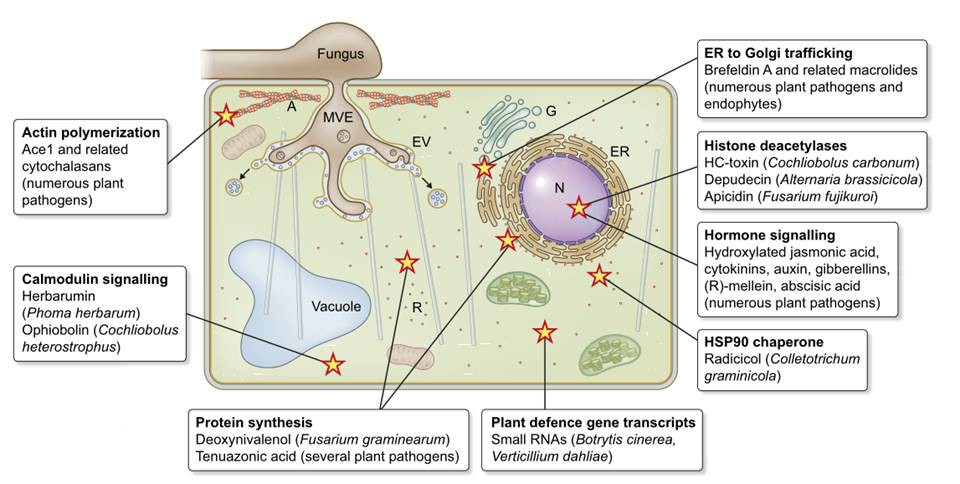 Fig. 1 Fungal non-proteinaceous effectors (NPEs) with potential effector-like functions during plant-fungal interactions (Collemare et al., 2019).
Fig. 1 Fungal non-proteinaceous effectors (NPEs) with potential effector-like functions during plant-fungal interactions (Collemare et al., 2019).
Study of pathogen SMs
We help discover pathogenic SMs that promote disease processes. We help analyze the transcriptomes and metabolomes of pathogens at different stages of pathogenic infiltration, from which we identify potential SM biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) and metabolite effectors.
We help validate the function of SMs. We can help construct pathogens with mutations in the target secondary metabolite and use mutated and unmutated pathogens for phytotoxicity assays. We help study the toxicity profile of purified SMs in plants. We can help construct heterologous hosts to express SMs for phytotoxicity assays. Our common heterologous hosts are Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus oryzae. Furthermore, we can offer the expression of pathogenic SMs in plants to study the role of SMs.
We help determine the structure of SMs. We have extensive experience in metabolite analysis and metabolite structure analysis. We can analyze the structure of pathogenic SMs using multiple methods, including three-dimensional imaging mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance, and X-ray diffraction.
Study of pathogen sRNAs
We help discover pathogenic sRNAs that promote disease processes. We help discover pathogenic sRNAs that regulate pathogen gene expression or host gene expression to enhance their virulence. Based on genetic information, we can help discover potential sRNAs, especially siRNAs. For example, we help discover the siRNAs encoded by fungi and oomycetes, which are mainly derived from transposons, inverted, tandem, or repeat regions, and effector coding regions.
We help determine the target mRNAs of sRNAs. We have extensive experience in RNA interference research design and experimental manipulation. We can flexibly use host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) and spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS) to help validate the target of sRNAs. We can also provide knocking down the sRNAs gene of pathogens for validation of target mRNAs' expression. We mainly use second-generation sequencing for the sequencing of sRNAs, and we mostly use qPCR to validate the expression of potential target mRNAs.
We help validate the function of sRNAs. After identifying the target mRNA, we help identify the protein encoded by the target mRNA and further validate the function.
Lifeasible helps to study the role of non-proteinaceous effectors in plant-pathogen interactions. We offer custom research services for potential SMs and sRNAs effectors. Please contact us to discuss the custom services.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024