Lifeasible helps to study key factors in plant-pathogen interactions and their mechanisms of action. Here we help study the role of plant oxylipins in plant-pathogen interactions.
Plant oxylipins are structurally diverse metabolites that are produced following the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. They play crucial developmental and defensive roles. Plant oxylipins include free and esterified oxylipins (Fig. 1). Plant oxylipins are produced under various stress conditions. Some oxylipins are essential components of plant signaling pathways, such as jasmonic acid, an important phytohormone. Some oxylipins have direct anti-pathogen effects. For example, oxylipins derived from the 9-lipoxygenase (9-LOX) and α-dioxygenase (α-DOX) pathways exhibit strong action against bacterial infections. Increasing our knowledge of plant oxylipins' specific actions could help develop plant agrochemicals. Lifeasible contributes to the study of plant oxylipins and provides services to help explore their role in plant-pathogen interactions.
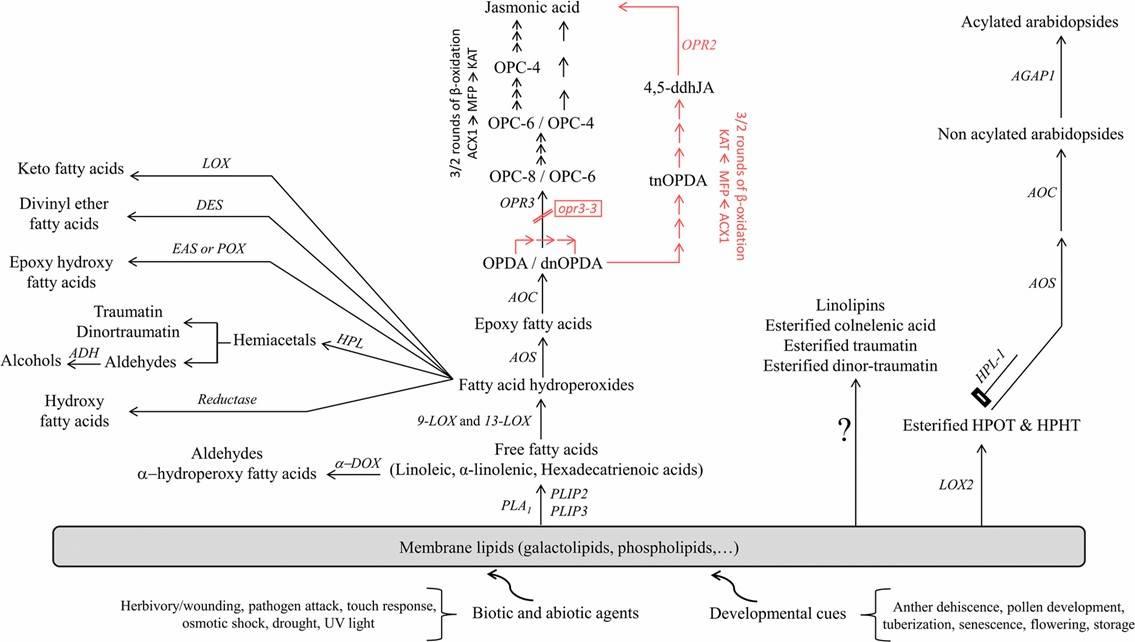 Fig. 1 Biosynthesis pathways of plant free and esterified oxylipins (Genva et al., 2019).
Fig. 1 Biosynthesis pathways of plant free and esterified oxylipins (Genva et al., 2019).
We help analyze changes in the type and content of plant oxylipins in plant-pathogen interactions. We also help to explore the mechanisms of plant protection-related effects of different plant oxylipins.
Analysis of plant oxylipins
Detection of changes in plant oxylipins after pathogen invasion can help identify oxylipins with plant protective functions. We offer quantitative and type analysis services for plant oxylipins.
We help with the extraction of plant oxylipins. Our standard extraction methods are phase partitioning using chloroform/methanol-based or hexane/2-propanol-based protocols and solid phase extraction steps using pre-packed C18 or NH2 columns. We pay strict attention to the occurrence of non-enzymatic oxidation during the extraction of oxylipins. We treat samples under an inert atmosphere (under streaming nitrogen or argon gas). We also avoid the non-specific de-esterification of esterified oxylipins by lipases. We strictly ensure that samples are processed at a low temperature.
For analyzing oxylipins, we can perform targeted analyses using various advanced instruments. We use high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS)/MS for analyses. For oxylipins that have a low abundance or have no intramolecular chromophores, we use gas chromatography (GC)-MS with electron ionization (EI) or chemical ionization (CI). At this point, the oxylipins need derivatization.
After quantitative analysis, we use nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for unknown oxylipins to help analyze their structure.
Investigating the signaling role of oxylipins
We help analyze the signaling role of oxylipins. After spraying different amounts of oxylipins or oxylipins analogs on plants, we help with plant transcriptomic, proteomic or metabolomic studies to help analyze the signaling role of oxylipins to be tested. We help detect the subcellular localization of oxylipins to help determine the mechanisms by which they exert their signaling effects, including stimulating defense gene expression or modifying proteins.
Investigating the no-signaling role of oxylipins
We help to test the direct effects of plant oxylipins on pathogens, including inhibition of growth, inhibition of spore germination, disruption of cell membranes, disruption of cell walls, and induction of oxidative bursts. To further confirm the effects, we also help test the host plant’s resistance to the pathogen after spraying with exogenous oxylipins.
Lifeasible offers professional plant oxylipin research services. We master validated research methods and have advanced testing equipment. Please contact us to start our collaboration.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024