Predatory fungi are a group of fungi that produce a variety of traps, including sticky nets, sticky balls, sticky branches, constriction rings, and three-dimensional fungal nets, to catch nematodes. To date, more than 380 species of predatory fungi have been reported from around the world, including members of the phyla Splanchomycetes, Ascomycetes, Stromatophora and Hemiptera. They are widely distributed worldwide and exist in various ecological environments, including agricultural soils, garden soils, forest soils, etc.
Lifeasible develops an advanced platform for analysis services for the control of nematodes by parasitic bacteria, which is equipped with advanced instruments and professional staff with a high standard. We customize featured services according to the customers' demand.
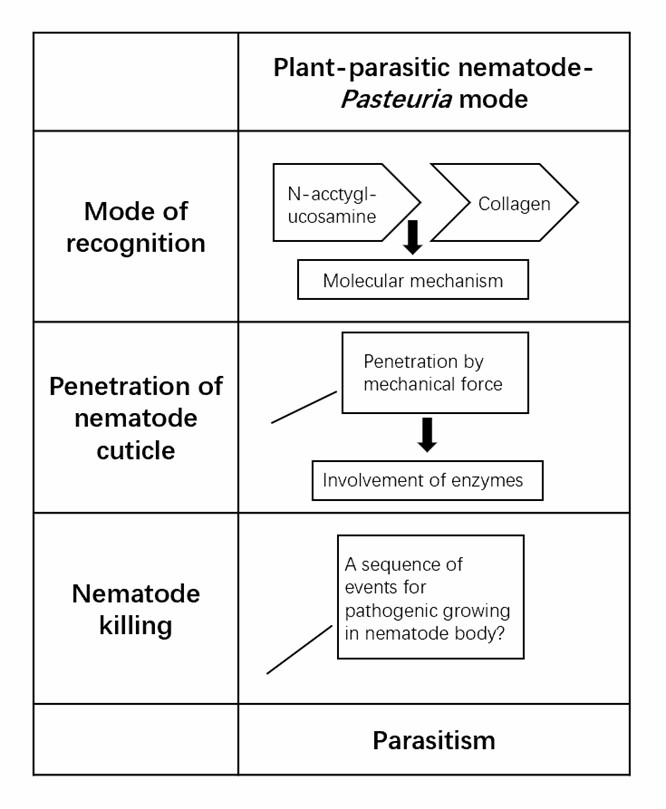 Fig.1 Pathogenic mechanism of typical bacterium-nematode interaction models.
Fig.1 Pathogenic mechanism of typical bacterium-nematode interaction models.
Lifeasible offers services covering the analysis of parasitic bacteria to meet your research demands. With years of experience in plant science, our professional platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024