The mouse is the most used animal model in the literature. The vast majority of the literature uses various strains of mice. This is because mice are 99% genetically similar to humans. Also, mice are small, inexpensive, have a diverse diet, and reproduce quickly. Researchers can study several generations of their offspring simultaneously in a relatively short period of time. Also, the physiology and genetics of mice have been extensively studied and can be easily compared to humans.
More importantly, techniques used to study genetics and specific gene functions, such as transgenic approaches, have been developed in mice for decades. Mouse models of many human diseases have been established to facilitate the study of pathogenesis and to assess the effects and toxicity of various drug candidates. Mouse genomes have been sequenced, and ChIP-seq techniques are often applied to mouse models to decode the mystery of protein-DNA binding.
Lifeasible, a world-renowned plant, and animal biotechnology company, has built a cutting-edge sequencing technology platform with state-of-the-art sequencing instruments and can spare no effort to provide you with customized mouse ChIP-seq services. Our service is designed to help you detect DNA segments that interact with histones, transcription factors, etc., on a genome-wide scale.
Our mouse ChIP-seq technology service is universal, easy to use, has high throughput and high quality and is capable of targeting various organ tissues and cells in mouse models for specific purposes.
Through an efficient ChIP analysis procedure, we investigated the chromosomal regions of five major transcription factors (ZIC2, OTX2, SOX2, POU5F1, and POU3F1) in mouse ectodermal stem cells, demonstrating their involvement in EpiSC maintenance and somatic cell development processes.
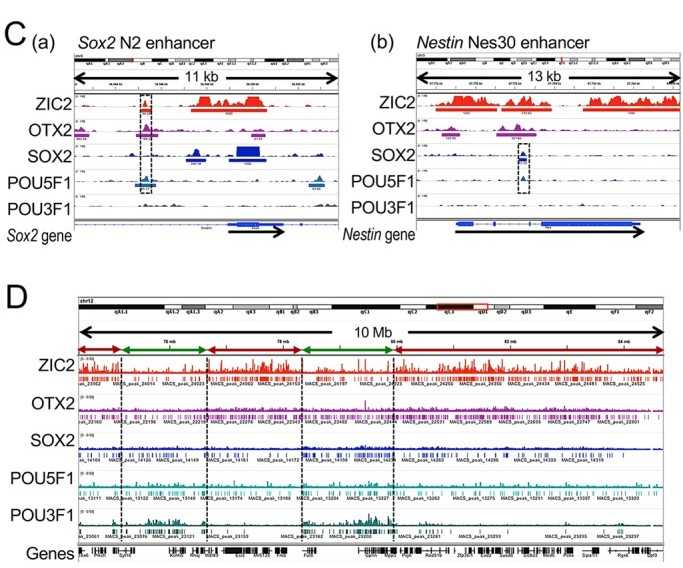 Figure 1. ChIP-seq data of five major transposable elements. (Matsuda, K, et al. 2017)
Figure 1. ChIP-seq data of five major transposable elements. (Matsuda, K, et al. 2017)
Through multiple chromatin immunoprecipitation and ChIP-seq, we annotated chromatin states during mouse fetal development and mapped chromatin dynamics view to describe the relationship between chromatin states and accessibility during developmental gene regulation. This mouse model of ChIP-seq can help scientists in the study of mammalian fetal developmental processes.
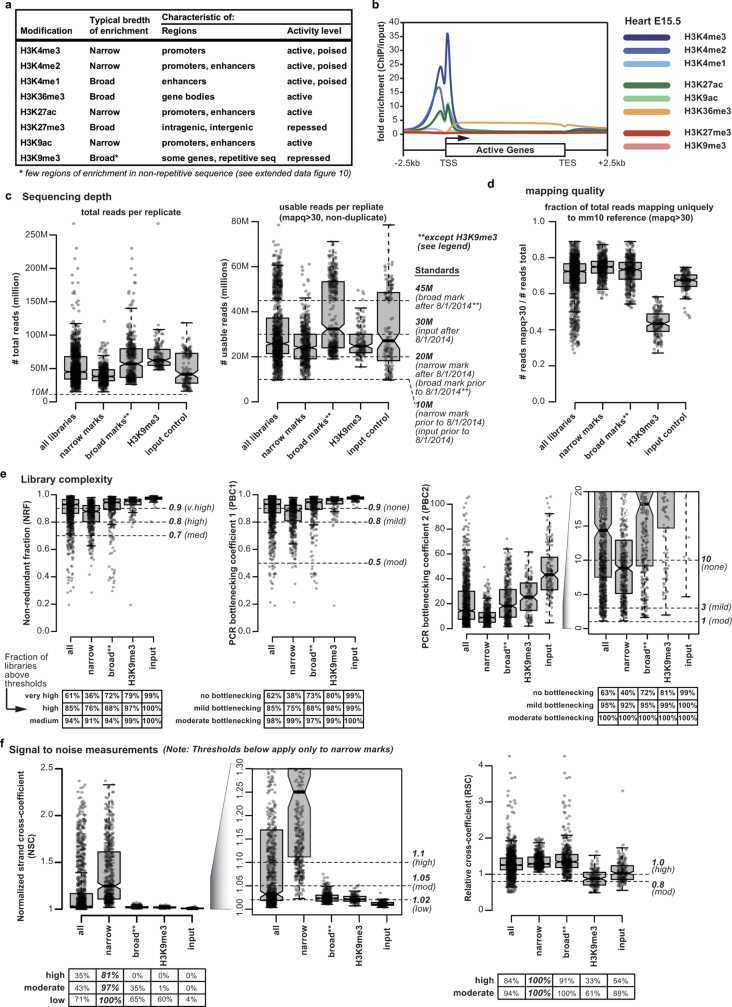 Figure 2. ChIP–seq data summary. (Gorkin, D. U, et al. 2020)
Figure 2. ChIP–seq data summary. (Gorkin, D. U, et al. 2020)
TFBS are critical for gene regulation, yet most TFBS remain unknown. To discover new TFBS, we sequenced mice using ChIP-seq technology and then analyzed the sequencing data to infer new TFBS.
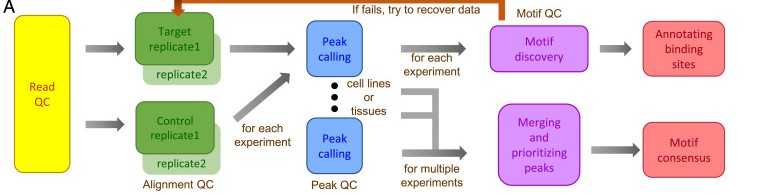 Figure 3. Flow chart of the detection of TFBS by ChIP-seq technology. (Yu, C. P, et al. 2021)
Figure 3. Flow chart of the detection of TFBS by ChIP-seq technology. (Yu, C. P, et al. 2021)
By performing ChIP-seq on mouse intestinal precursor cells, we revealed new potential genes RABGGTB, BRD3, TGFB1, HRAS, and GRB2 that play a role in developing the enteric nervous system and congenital megacolonosis.
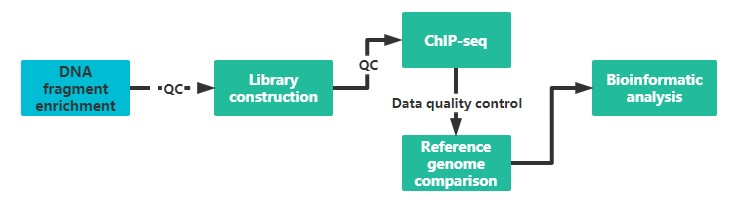
It is recommended to provide two sample preparations, if possible, to ensure the quality and continuity of the experiment.
Lifeasible's animal-oriented sequencing technology platform can provide you with various mouse ChIP-seq solutions to help you perform functional enrichment analysis, predict the function of specific proteins, map histone chromosome binding, and detect episomal modifications of DNA. For questions, inquiries, or collaboration, please feel free to contact us.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
STU-CRISPR System Improves Plant Genome Editing Efficiency
April 19, 2024
Application of Exosomes in Facial Beauty
April 12, 2024